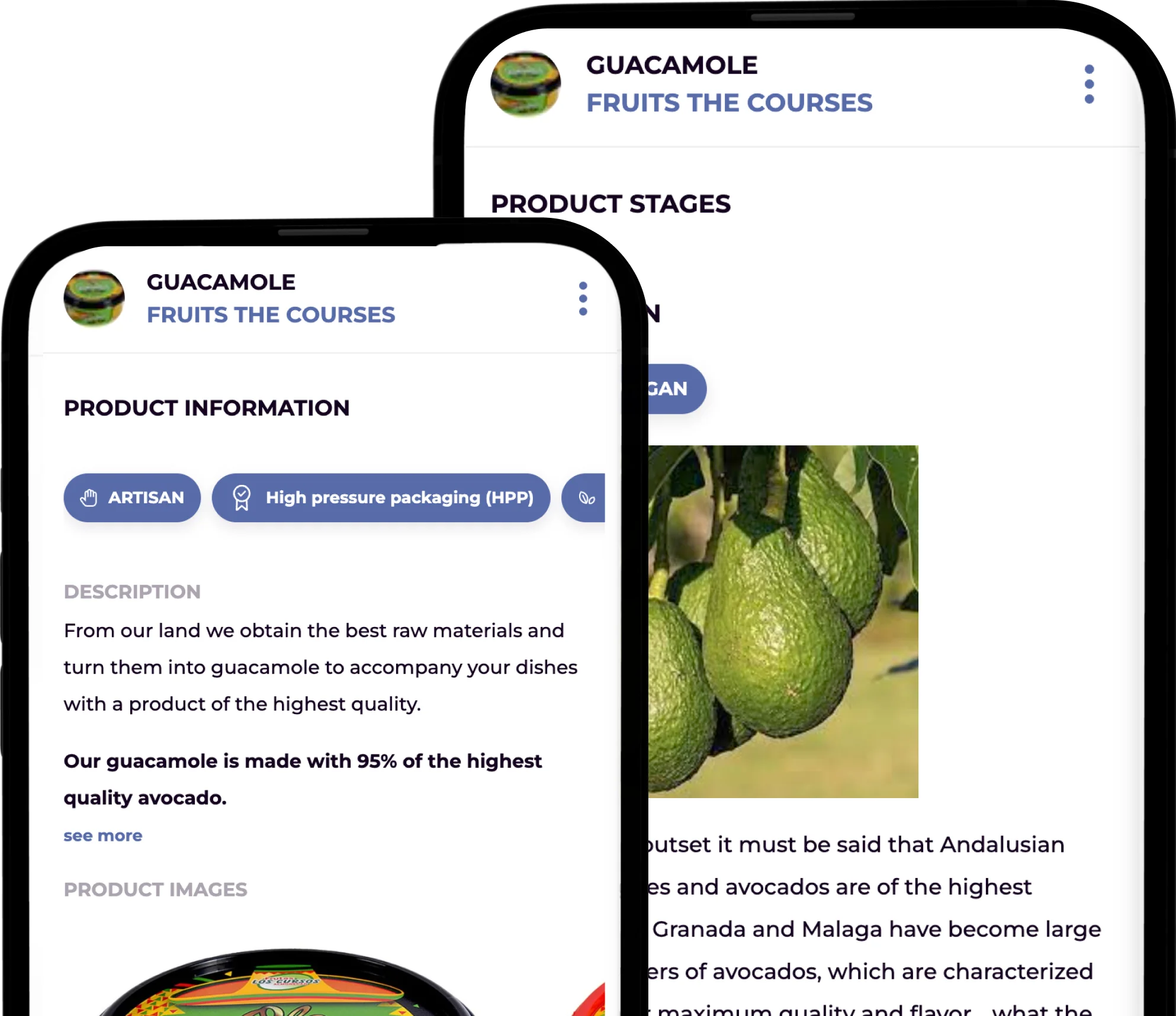
Recent EU regulations require wines and aromatized wine products made after December 8, 2023, to list ingredients and nutritional information, ensuring consumers have easy access to essential details.
If you’re a winery or a customer looking to navigate the new EU wine labeling regulations, this article provides a practical approach to compliance using QR codes and digital labels (e-labels).
Using QR Codes for EU Wine Compliance
Wine producers are increasingly adopting QR codes and digital labels for regulatory compliance due to two main advantages:
- Cost Savings: Dynamic QR codes reduce the need for frequent updates to physical label designs, saving time and money.
- Future-Proofing: QR codes allow for immediate label implementation, with the ability to update linked digital content (e-labels) as regulations change.
This approach, known as the “e-label solution,” includes QR code generation and the creation of compliant digital labels.
Compliance involves a series of steps, which can be completed in any order. We’ll explore each step in detail to provide a clear guide for compliance.
Due to their ongoing change, being current on regulations and guidelines is fundamental. This remains relevant, especially given the December 8, 2023 compliance date.
Step 1: Organize Your Wine Product Information
The first step in complying with the new EU wine labeling regulations is to organize all the necessary product information for input into your e-label solution. This can be done using a spreadsheet or database. The required information for digital wine labels includes both mandatory and optional details:
Product Information
- Wine Variety: Specify the type of wine.
- Nutritional Information: Provide details on energy, fats, carbohydrates, proteins, and salt.
- Allergen Declaration: List any allergens present in the wine.
- Origin Country: Indicate the country where the wine is produced.
- Importer, Bottler, and Producer: Identify the key entities involved in the wine’s production and distribution.
- Geographical Indications: Mention any geographical indications associated with the wine.
- Vintage Year: State the year of the wine’s production.
- Alcohol by Volume (ABV): Provide the percentage of alcohol content.
- Net Quantity: Specify the volume of wine in milliliters.
- Sugar Content: Indicate the amount of sugar present in the wine.
- Vine Variety: Mention the specific vine variety used for that vintage.
- Product Description: Provide a brief description of the wine.
- Date of Expiration: Includes an expiration date for wines with an ABV less than 10%.
Serving Sizes
The law requires nutritional and energy information based on a 100ml serving. Information based on standard serving sizes like 125ml, 175ml, and 250ml can also be provided for consumer convenience.
Ingredients
The e-label must list ingredients in descending order of weight, as per Article 18 of Regulation (EU) 1169/2011. Additives should be categorized accordingly.
Nutritional Facts
Prepare the following nutritional details for each wine product:
- Energy
- Saturates
- Sugars
- Fat
- Carbohydrates
- Protein
- Salt
Your e-label solution may provide a calculator for energy, or you can specify it directly.
Allergens and Intolerances
Any allergens or intolerances must be displayed on both the physical and e-label labels.
Additives and Processing Aids
From December 8, 2023, listing acidity regulators and stabilizing agents with no more than three alternative ingredients in the ingredients list will be permissible, provided at least one of those additives is present in the final product.
Translations
E-labels must be available in the languages used in the markets where the products are sold. Most global brands are creating translated versions of their e-labels in all 24 EU languages. Depending on your solution, you may need to organize your product information and ingredients translations at this stage.
Once you have organized the required information for each of your wine products, you can proceed to the next step in the compliance process.
Step 2: Enter Wine Product (SKU) Data into Your Software Solution and Review Translations
Efficiently transferring wine product information into your e-label solution is a critical step in ensuring compliance with EU regulations. There are three primary methods to consider, each suited to different scales of operation:
- Manual Entry: Best for a limited number of SKUs. For instance, if you have just 10 different wines, you can manually copy and paste details like wine variety, ABV, and nutritional information from your organized spreadsheet directly into the software.
- Bulk Upload: Ideal for a larger inventory. If you’re managing 50 or more SKUs, you can save time by uploading a CSV file containing all the necessary product details into your e-label solution. This method helps prevent manual errors and streamlines the data entry process.
- API Integrations: Recommended for extensive inventories and when seamless data synchronization is needed. For example, if you have over 100 SKUs and use a centralized database for your product information, API integration can automatically transfer updated data into your e-label solution, ensuring real-time accuracy and compliance.
Each method offers its advantages, depending on the size of your inventory and the capabilities of your e-label solution. As you proceed with this step, consider the scale of your operation and choose the method that best fits your needs.
Step 3: Generate and Download QR Codes
A unique digital label (e-label) and QR code are required for each wine product (SKU).
If your brand has a product line of five wines, each with distinct characteristics, you’ll create five e-labels and corresponding QR codes. While some wineries might explore serialized QR codes for advanced tracking, this practice is not yet widespread.
It’s essential to ensure that the QR codes are in a format compatible with your label printing process, facilitating easy integration.
Step 4: QR Code Integration and Printing
For wineries needing to expedite label printing, starting with the generation and integration of QR codes into designs is practical. Ensuring control over the QR codes through your software or system allows for subsequent adjustments to comply fully with regulations.
- Placement: The QR code is typically placed on the back label to maintain the brand’s visual identity. This placement ensures that the front label remains focused on branding and product presentation.
- Engagement and Clarity: Enhance user engagement by incorporating an “i” symbol or phrases like “Scan for info” near the QR code, providing clear instructions for consumers. When adding a call-to-action, ensure its relevance across all regions where the wine will be marketed, as this enhances the user’s understanding and interaction with the QR code.
- Sizing and Resolution: The recommended dimensions for QR codes are between 13mm x 13mm and 16mm x 16mm, excluding the quiet zone, which is essential for scanability. Printing at a high resolution of 300 dpi or higher ensures that the QR code remains clear and functional when printed on the label.
- Color and Contrast: A standard black QR code on a white background offers the best contrast for easy scanning. While other dark colors on light backgrounds may be used, they should be tested for scanability. If using inverted colors, like white on black, sufficient contrast is necessary to maintain readability.
- Creative Design: Although QR codes are square, creative designs can incorporate them into non-square shapes, such as a rotated square or a parallelogram diamond. It’s important to maintain the required quiet zone around the QR code to ensure it remains scannable.
By adhering to these guidelines and integrating QR codes into your wine labels, your products will be well-equipped to meet EU regulatory requirements, ensuring a smooth and efficient compliance process.
Additional Considerations for E-Label Compliance
When it comes to digital wine labels and QR codes, the possibility of switching e-label vendors after QR codes have been printed and applied to wines is a crucial consideration. The extent of your flexibility in this scenario largely depends on your initial implementation strategy.
Imagine starting with e-label Solution Provider A and later wanting to switch to Provider B. For new wines, generating e-labels and QR codes with Provider B is straightforward. However, for wines already labeled with QR codes from Provider A, customers scanning those codes would be directed to Provider A’s controlled website.
Implementation Approaches
- Static QR Codes: These QR codes link to a fixed URL and offer no flexibility for future changes. To prevent vendor lock-in, it’s advisable to avoid this option.
- Dynamic QR Codes with Redirect Option: These QR codes can be redirected to a different URL in the future, providing more flexibility if you decide to switch vendors.
- Using Your Domain: Incorporating your domain in the QR codes gives you complete control, enabling seamless transitions between e-label solution providers.
Options for Existing Labels
- Changing the URL might be impossible if the QR code is static, resulting in complete vendor lock-in.
- If Provider A offers URL redirection services, scanning a QR code from Provider A could redirect customers to Provider B’s e-label. However, this depends on Provider A’s reliability and willingness to provide this service.
- By using your own domain in the QR codes, you retain control over the website address inside the QR code, eliminating vendor lock-in concerns.
QR Code for Multiple Purposes
While your e-label can link directly to your website, it cannot link to pages with marketing information such as webshops, product sales, or loyalty programs. The definition of “marketing information” remains unspecified by regulators.
Requirements for Global Wine Brands
Global wine brands seeking compliance typically require the following e-label solution features:
- Bulk Upload and APIs: These features save time and reduce the risk of errors in manual entry.
- Auto-Translation and Translation Management: Ensures compliance and saves time.
- Future Compliance Solutions: Anticipates emerging laws and regulations in different countries.
- Intelligent URL Scan Destination: Provides a relevant scan experience for non-EU consumers.
- GS1 Compatibility: Ensures compatibility with emerging standards.
- Security and Uptime Guarantees: Ensures reliability and availability of the e-label solution.
- Global and Multilingual Support: Offers comprehensive support for diverse markets.
By considering these aspects and choosing the right implementation approach, wine brands can ensure flexibility and compliance with digital wine labels and QR codes.
Conclusion
At SwearIt, we’re dedicated to simplifying the compliance process for EU wine labeling regulations with our innovative technology and expertise. Discover more about our solutions, register for our complimentary tool, or reach out to explore our enterprise options.